What Is Helium Bohr Model? Simplified Explanation
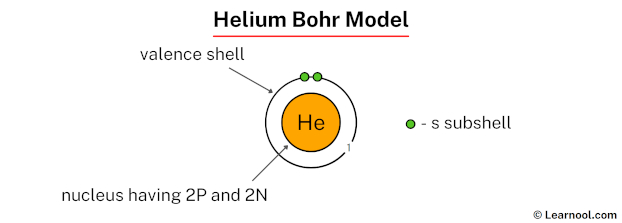
The Helium Bohr model is an extension of the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom, applied to helium, which is the second simplest atom after hydrogen. To understand the Helium Bohr model, let’s first briefly explore the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom.
Introduction to the Bohr Model of Hydrogen
In 1913, Niels Bohr proposed a model for the hydrogen atom that revolutionized the understanding of atomic structure. According to the Bohr model, the hydrogen atom consists of a small, heavy nucleus (a proton) around which a single electron orbits at a fixed distance. This model posits that the electron can only occupy specific energy levels (or shells) and that it can jump from one energy level to another by emitting or absorbing energy in the form of photons.
Applying the Bohr Model to Helium
Helium is the next element after hydrogen in the periodic table, with an atomic number of 2. This means a helium atom has 2 protons in its nucleus and, when neutral, 2 electrons orbiting the nucleus. The application of the Bohr model to helium involves understanding how these two electrons arrange themselves around the nucleus.
Key Assumptions:
- Energy Levels: Similar to the hydrogen atom, electrons in a helium atom occupy specific energy levels or shells.
- Electron Arrangement: The two electrons in helium occupy the lowest available energy levels. According to the Bohr model and the Pauli Exclusion Principle (which states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of quantum numbers), both electrons would occupy the first energy level (or 1s orbital), with their spins being opposite (one spin up and one spin down).
Simplified Explanation of the Helium Bohr Model:
- Nucleus: The helium nucleus consists of 2 protons and 2 neutrons, making it 4 times heavier than the hydrogen nucleus.
- Electron Configuration: Both electrons are in the first energy level (1s^2 configuration), where they are most stable, with one electron having a spin of +1⁄2 and the other -1⁄2.
- Energy Levels and Stability: The electrons in the 1s orbital are at a lower energy state than if they were in any higher energy level, contributing to the stability of the helium atom.
- Ionization Energy: To remove an electron from a helium atom, significant energy is required, reflecting the strong attraction between the electrons and the nucleus.
Limitations and Beyond
While the Bohr model provides a simplified and useful understanding of atoms like helium, it is not without its limitations. The model does not account for the electron’s spin or the complexities introduced by more than one electron. Quantum mechanics, developed later, provides a more accurate and comprehensive description of atomic structure, including the behavior of electrons in multi-electron atoms like helium.
Conclusion
The Helium Bohr model represents an early attempt to understand the structure of atoms beyond hydrogen. Although it simplifies the arrangement of electrons in helium and doesn’t fully capture the intricacies of electron behavior, it laid foundational groundwork for later, more sophisticated models like quantum mechanics. Understanding the Helium Bohr model can serve as a stepping stone for exploring more complex atomic structures and the principles governing the behavior of electrons within them.
What are the main differences between the Bohr model of hydrogen and helium?
+The main differences lie in the number of electrons and the arrangement of these electrons. Hydrogen has one electron, while helium has two, which are arranged in the 1s orbital with opposite spins.
What is the significance of the Bohr model in understanding atomic structure?
+The Bohr model is significant because it introduced the concept of energy levels and quantized energy states for electrons, laying the groundwork for later, more precise models of atomic structure.
How does the Helium Bohr model relate to more advanced models of atomic structure?
+The Helium Bohr model is a stepping stone towards more complex and accurate models. Quantum mechanics, for example, builds upon the foundational concepts introduced by the Bohr model but provides a more detailed and accurate description of electron behavior in atoms like helium.
In exploring the Helium Bohr model, it becomes clear that while it represents an important step in the development of atomic theory, it is part of a broader journey towards understanding the intricate and complex world of atomic physics.