Trial Balance Guide: Accurate Financials Guaranteed

The humble trial balance - a fundamental concept in accounting that has been the backbone of financial statement preparation for centuries. Yet, despite its importance, many accountants and bookkeepers often view the trial balance as a mere formality, a checkbox to be marked off before diving into the “real” work of financial analysis. However, this couldn’t be further from the truth. A well-prepared trial balance is the foundation upon which all financial statements are built, and its accuracy is crucial for ensuring the reliability of a company’s financial reports.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of trial balances, exploring their purpose, preparation, and importance in the accounting process. We will also discuss common errors to avoid and provide tips for ensuring accuracy and efficiency in trial balance preparation.
What is a Trial Balance?
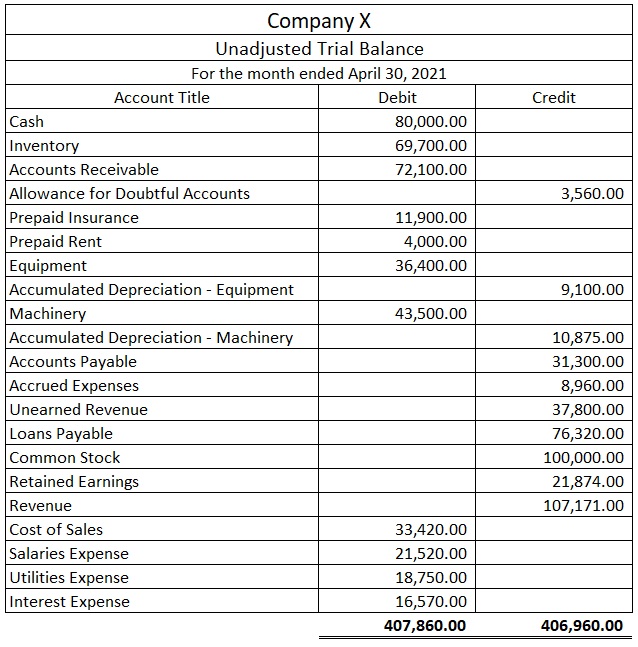
A trial balance is a list of all general ledger accounts and their corresponding debit or credit balances. It is prepared at the end of an accounting period, typically on a monthly, quarterly, or annual basis, and serves as a preliminary step in the preparation of financial statements. The trial balance is used to ensure that the debits and credits in the general ledger are equal, which is a fundamental principle of double-entry accounting.
Why is a Trial Balance Important?
A trial balance is essential for several reasons:
- Error detection: A trial balance helps to detect errors in the general ledger, such as incorrect postings, misclassifications, or omissions. By identifying these errors, accountants can correct them before preparing financial statements.
- Balance verification: A trial balance verifies that the debits and credits in the general ledger are equal, which is critical for ensuring the accuracy of financial statements.
- Financial statement preparation: A trial balance provides the necessary information for preparing financial statements, such as the balance sheet and income statement.
How to Prepare a Trial Balance
Preparing a trial balance involves the following steps:
- Extract general ledger accounts: Extract all general ledger accounts, including asset, liability, equity, revenue, and expense accounts.
- Determine account balances: Determine the balance of each account, either by manually calculating the balance or by using accounting software.
- Classify accounts: Classify each account as either a debit or credit balance.
- Prepare the trial balance: Prepare the trial balance by listing all accounts and their corresponding balances.
Common Errors to Avoid
When preparing a trial balance, there are several common errors to avoid:
- Incorrect account classification: Incorrectly classifying an account as a debit or credit balance can lead to errors in the trial balance.
- Omissions: Omitting accounts or transactions can result in an incomplete trial balance.
- Incorrect balances: Incorrectly calculating account balances can lead to errors in the trial balance.
- Failure to reconcile: Failing to reconcile the trial balance with the general ledger can lead to errors in financial statements.
Tips for Ensuring Accuracy and Efficiency
To ensure accuracy and efficiency in trial balance preparation, follow these tips:
- Use accounting software: Use accounting software to automate the trial balance preparation process and reduce the risk of errors.
- Regularly review and reconcile: Regularly review and reconcile the trial balance with the general ledger to ensure accuracy.
- Use a standardized format: Use a standardized format for preparing the trial balance to ensure consistency and readability.
- Double-check calculations: Double-check calculations and account balances to ensure accuracy.
Real-World Example
To illustrate the importance of a trial balance, consider the following example:
Suppose a company, XYZ Inc., has a general ledger that includes the following accounts:
| Account | Debit Balance | Credit Balance |
|---|---|---|
| Cash | $10,000 | |
| Accounts Receivable | $20,000 | |
| Accounts Payable | $15,000 | |
| Revenue | $50,000 | |
| Expenses | $30,000 |
To prepare the trial balance, XYZ Inc. would list all accounts and their corresponding balances, as follows:
| Account | Debit Balance | Credit Balance |
|---|---|---|
| Cash | $10,000 | |
| Accounts Receivable | $20,000 | |
| Accounts Payable | $15,000 | |
| Revenue | $50,000 | |
| Expenses | $30,000 | |
| Total | $60,000 | $65,000 |
In this example, the trial balance reveals that the debits and credits are not equal, indicating an error in the general ledger. By identifying and correcting this error, XYZ Inc. can ensure the accuracy of its financial statements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a trial balance is a critical component of the accounting process, providing a foundation for accurate financial statement preparation. By understanding the purpose, preparation, and importance of a trial balance, accountants and bookkeepers can ensure the reliability of financial reports and make informed decisions. Remember to avoid common errors, follow tips for ensuring accuracy and efficiency, and use accounting software to automate the trial balance preparation process.
What is the purpose of a trial balance?
+The purpose of a trial balance is to ensure that the debits and credits in the general ledger are equal, which is a fundamental principle of double-entry accounting. It also helps to detect errors in the general ledger and provides a foundation for preparing financial statements.
How often should a trial balance be prepared?
+A trial balance should be prepared at the end of each accounting period, typically on a monthly, quarterly, or annual basis.
What are some common errors to avoid when preparing a trial balance?
+Common errors to avoid when preparing a trial balance include incorrect account classification, omissions, incorrect balances, and failure to reconcile the trial balance with the general ledger.
How can accounting software help with trial balance preparation?
+Accounting software can automate the trial balance preparation process, reduce the risk of errors, and provide a standardized format for preparing the trial balance.
What is the difference between a trial balance and a balance sheet?
+A trial balance is a list of all general ledger accounts and their corresponding balances, while a balance sheet is a financial statement that presents the financial position of a company at a specific point in time. The trial balance is used to prepare the balance sheet, as well as other financial statements.



