Tertbutyl Chloride Uses
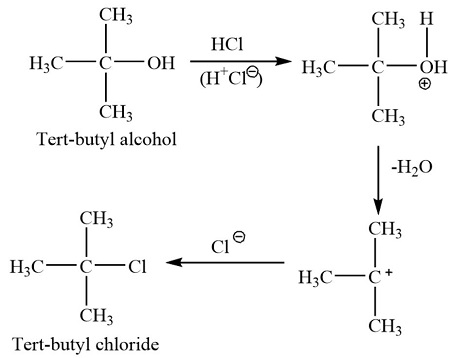
Tertbutyl chloride, also known as 2-methylpropan-2-yl chloride, is a colorless, flammable, and highly reactive organic compound with a wide range of applications in various industries. Its unique chemical properties make it an essential intermediate in the synthesis of numerous valuable chemicals, materials, and pharmaceuticals. This article will delve into the diverse uses of tertbutyl chloride, exploring its role in chemical synthesis, its applications in different sectors, and the safety considerations associated with its handling.
Chemical Synthesis
Tertbutyl chloride is a versatile reagent in organic chemistry, used in the synthesis of complex molecules due to its ability to undergo various reactions, including nucleophilic substitution, elimination, and addition reactions. It serves as a valuable intermediate in the preparation of tert-butyl esters, ethers, and other tert-butyl derivatives, which are crucial in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and fine chemicals.
One of the notable applications of tertbutyl chloride in chemical synthesis is in the production of tert-butyl hydroperoxide, a strong oxidizing agent used in various oxidation reactions. The synthesis involves the reaction of tertbutyl chloride with oxygen in the presence of a catalyst, resulting in tert-butyl hydroperoxide, which is then used as an initiator in polymerization reactions or as an oxidant in organic synthesis.
Pharmaceutical Applications
In the pharmaceutical industry, tertbutyl chloride is used as an intermediate in the synthesis of certain drugs and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Its tert-butyl group can be used to protect sensitive functional groups during synthesis, which can then be deprotected under specific conditions to yield the desired pharmaceutical compound. This protecting group strategy is crucial in the synthesis of complex molecules, ensuring that certain parts of the molecule are not affected by reaction conditions meant for other parts.
Material Science Applications
Tertbutyl chloride plays a significant role in material science, particularly in the production of polymers and resins. It is used in the synthesis of monomers that are then polymerized to form polymers with specific properties, such as resistance to heat, chemicals, or impact. For instance, tert-butyl methacrylate, synthesized from tertbutyl chloride, is a monomer used in the production of acrylic resins and polymers, which find applications in coatings, adhesives, and biomedical devices.
Agrochemical Applications
In agrochemistry, tertbutyl chloride is involved in the synthesis of herbicides, pesticides, and other crop protection chemicals. The tert-butyl group is often incorporated into the molecular structure of these compounds to enhance their biological activity, stability, or selectivity. For example, certain herbicides containing the tert-butyl moiety have been developed to exhibit high efficacy against specific weeds while being safer for crops.
Safety Considerations
Despite its numerous applications, tertbutyl chloride poses significant safety risks due to its flammability, corrosivity, and potential to cause skin and eye irritation. It is also considered a hazardous air pollutant, necessitating careful handling and storage to minimize exposure to workers and the environment. Protective equipment, including gloves, goggles, and respirators, should be used when handling tertbutyl chloride, and operations involving this chemical should be conducted in well-ventilated areas or under fume hoods.
Conclusion
Tertbutyl chloride is a multifaceted chemical intermediate with a broad spectrum of applications across various industries, from chemical synthesis and pharmaceuticals to material science and agrochemistry. Its versatility stems from its chemical reactivity, which allows it to participate in a wide range of reactions, making it a valuable tool for the synthesis of complex molecules and materials. However, its handling requires careful attention to safety protocols due to its hazardous properties. As research and development continue to advance, the role of tertbutyl chloride in creating innovative materials, drugs, and technologies is likely to expand, underscoring its importance in the chemical industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary uses of tertbutyl chloride?
+Tertbutyl chloride is primarily used as an intermediate in chemical synthesis, particularly in the production of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and polymers. Its applications span across various industries due to its versatility in undergoing different chemical reactions.
What safety precautions should be taken when handling tertbutyl chloride?
+Handling tertbutyl chloride requires careful attention to safety. It is recommended to wear protective gear, including gloves, goggles, and respirators. Operations should be conducted in well-ventilated areas or under fume hoods to minimize exposure due to its flammability and potential to cause irritation.
Can tertbutyl chloride be used in the synthesis of complex molecules?
+Yes, tertbutyl chloride is a valuable reagent in the synthesis of complex molecules. Its tert-butyl group can be used as a protecting group, allowing for selective reactions at specific sites of the molecule without affecting sensitive functional groups.
What are the implications of tertbutyl chloride in material science?
+In material science, tertbutyl chloride is used in the synthesis of monomers for polymers and resins, contributing to the development of materials with specific properties such as heat resistance, chemical stability, and impact resistance. These materials find applications in various industries, including coatings, adhesives, and biomedical devices.
The applications of tertbutyl chloride highlight its significance in the chemical industry, serving as a bridge between basic chemical synthesis and the development of complex materials and pharmaceuticals. Its role in facilitating the synthesis of a wide range of valuable compounds underscores its importance for future innovations in chemistry and materials science.



