Potential Divider Formula Explained
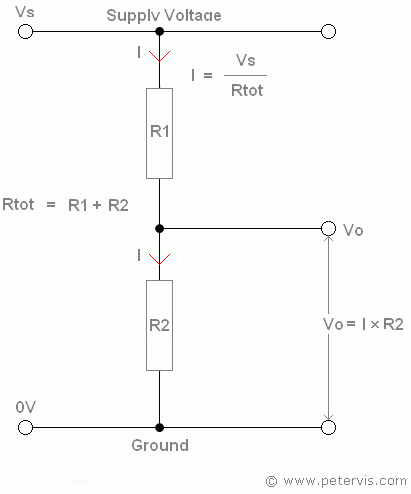
The potential divider formula, also known as the voltage divider formula, is a fundamental concept in electronics that allows us to calculate the output voltage of a circuit based on the input voltage and the resistances of the circuit components. In this explanation, we will delve into the details of the potential divider formula, its derivation, and its practical applications.
Introduction to Potential Dividers
A potential divider is a simple circuit that consists of two resistors connected in series across a voltage source. The output voltage is taken across one of the resistors, and the ratio of the output voltage to the input voltage is determined by the ratio of the resistances. Potential dividers are widely used in electronic circuits for voltage reduction, signal attenuation, and impedance matching.
Derivation of the Potential Divider Formula
To derive the potential divider formula, let’s consider a basic potential divider circuit consisting of two resistors, R1 and R2, connected in series across a voltage source, Vin. The output voltage, Vout, is taken across resistor R2.
Using Ohm’s law, we can write the current flowing through the circuit as:
I = Vin / (R1 + R2)
The voltage drop across resistor R1 is:
V1 = I * R1
Substituting the expression for I, we get:
V1 = (Vin / (R1 + R2)) * R1
The voltage drop across resistor R2 is:
V2 = I * R2
Substituting the expression for I, we get:
V2 = (Vin / (R1 + R2)) * R2
Since the output voltage, Vout, is taken across resistor R2, we can write:
Vout = V2
Substituting the expression for V2, we get:
Vout = (Vin / (R1 + R2)) * R2
Simplifying the expression, we get the potential divider formula:
Vout = Vin * (R2 / (R1 + R2))
Practical Applications of Potential Dividers
Potential dividers have numerous practical applications in electronic circuits. Some of the most common applications include:
- Voltage reduction: Potential dividers can be used to reduce the voltage of a signal or a power supply. For example, a potential divider can be used to reduce the voltage of a 12V power supply to 5V.
- Signal attenuation: Potential dividers can be used to attenuate the amplitude of a signal. For example, a potential divider can be used to reduce the amplitude of an audio signal to prevent clipping.
- Impedance matching: Potential dividers can be used to match the impedance of a circuit to a load or a source. For example, a potential divider can be used to match the impedance of a microphone to a preamplifier.
Design Considerations for Potential Dividers
When designing a potential divider, there are several factors to consider:
- Resistor values: The values of the resistors, R1 and R2, determine the output voltage and the current flowing through the circuit. The resistor values should be chosen such that the current flowing through the circuit is within the safe operating range of the components.
- Voltage rating: The voltage rating of the resistors and the output voltage should be considered when designing a potential divider. The voltage rating of the resistors should be higher than the output voltage to prevent damage to the components.
- Power dissipation: The power dissipation of the resistors should be considered when designing a potential divider. The power dissipation of the resistors should be within the safe operating range of the components to prevent overheating.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the potential divider formula is a fundamental concept in electronics that allows us to calculate the output voltage of a circuit based on the input voltage and the resistances of the circuit components. The formula has numerous practical applications in electronic circuits, including voltage reduction, signal attenuation, and impedance matching. When designing a potential divider, it’s essential to consider the resistor values, voltage rating, power dissipation, and tolerances to ensure that the output voltage is accurate and reliable.
FAQ Section
What is the purpose of a potential divider?
+The purpose of a potential divider is to reduce the voltage of a signal or a power supply, attenuate the amplitude of a signal, or match the impedance of a circuit to a load or a source.
How do I calculate the output voltage of a potential divider?
+The output voltage of a potential divider can be calculated using the formula: Vout = Vin * (R2 / (R1 + R2)), where Vin is the input voltage, R1 and R2 are the resistances of the circuit components, and Vout is the output voltage.
What factors should I consider when designing a potential divider?
+When designing a potential divider, you should consider the resistor values, voltage rating, power dissipation, and tolerances to ensure that the output voltage is accurate and reliable.
Future Developments in Potential Dividers
The development of new materials and technologies is expected to improve the performance and efficiency of potential dividers. For example, the use of nanomaterials and graphene is expected to increase the accuracy and reliability of potential dividers. Additionally, the development of new circuit topologies and designs is expected to improve the efficiency and reduce the size of potential dividers.
Step-by-Step Guide to Designing a Potential Divider

- Determine the input voltage and the desired output voltage.
- Choose the resistor values based on the desired output voltage and the current flowing through the circuit.
- Consider the voltage rating and power dissipation of the resistors.
- Calculate the output voltage using the potential divider formula.
- Verify the accuracy of the output voltage using a multimeter or an oscilloscope.
Key Takeaways
- The potential divider formula is a fundamental concept in electronics that allows us to calculate the output voltage of a circuit based on the input voltage and the resistances of the circuit components.
- Potential dividers have numerous practical applications in electronic circuits, including voltage reduction, signal attenuation, and impedance matching.
- When designing a potential divider, it’s essential to consider the resistor values, voltage rating, power dissipation, and tolerances to ensure that the output voltage is accurate and reliable.
- The development of new materials and technologies is expected to improve the performance and efficiency of potential dividers.
