Food Web In The Temperate Forest
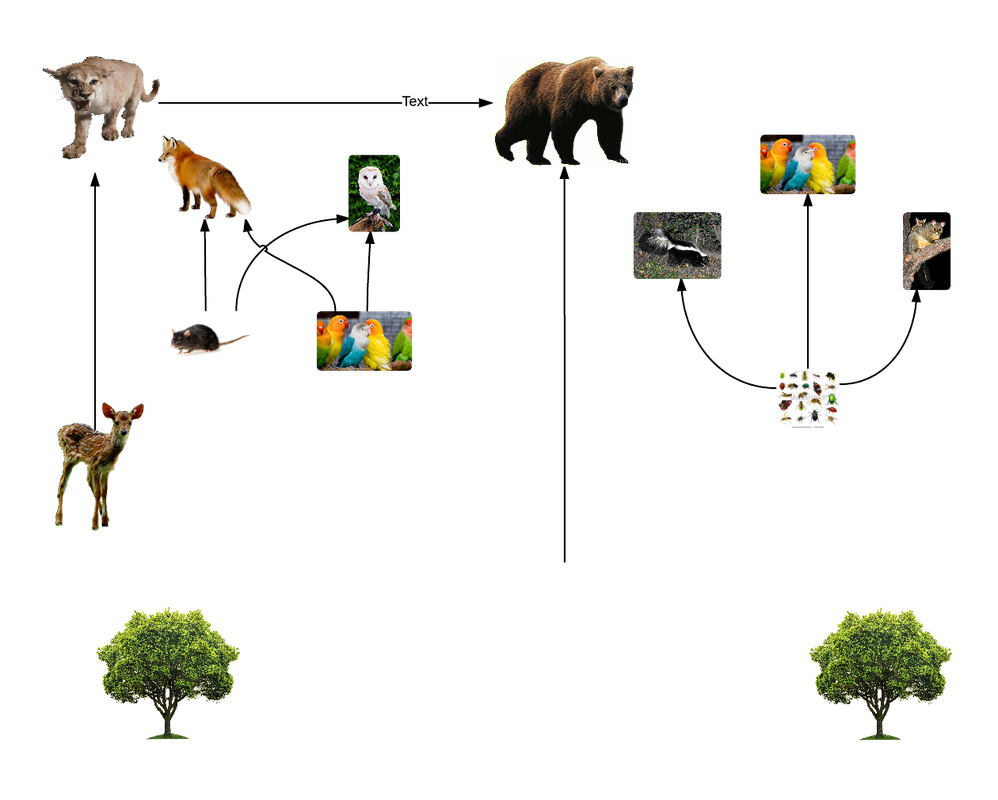
The temperate forest, characterized by its moderate climate and diverse range of plant and animal species, is home to a complex and dynamic food web. This intricate network of relationships between predators and prey, producers and consumers, is essential for maintaining the balance and health of the ecosystem.
At the base of the food web are the producers, primarily plants such as trees, shrubs, and herbaceous species. These organisms use sunlight, water, and nutrients from the soil to produce energy through photosynthesis. In the temperate forest, common producers include oak, beech, and maple trees, as well as understory plants like ferns and wildflowers.
The primary consumers in the temperate forest food web are herbivores, which feed on the producers. These herbivores can be further divided into two categories: grazers and browsers. Grazers, such as deer and rabbits, feed on grasses, leaves, and other vegetation, while browsers, like squirrels and birds, eat seeds, nuts, and fruits. Other primary consumers include insects like caterpillars and beetles, which feed on plant tissues.
Secondary consumers, which feed on primary consumers, are an essential component of the food web. These predators help regulate the populations of herbivores, preventing any one species from dominating the ecosystem. In the temperate forest, common secondary consumers include carnivores like foxes, coyotes, and owls, as well as omnivores like raccoons and opossums. These animals feed on a variety of prey, from insects and small mammals to birds and other vertebrates.
Tertiary consumers, which feed on secondary consumers, are at the top of the food web. These apex predators play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem, as they regulate the populations of secondary consumers. In the temperate forest, examples of tertiary consumers include large carnivores like bears and mountain lions, as well as birds of prey like hawks and eagles.
In addition to these trophic levels, the temperate forest food web also includes decomposers, which break down dead organic matter into nutrients that can be reused by producers. Decomposers like fungi, bacteria, and earthworms are essential for recycling nutrients and maintaining soil fertility.
The food web in the temperate forest is also influenced by abiotic factors, such as climate, soil quality, and topography. For example, changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can impact the growth and productivity of producers, which in turn affects the populations of consumers. Similarly, soil quality and topography can influence the distribution and abundance of different species, shaping the structure of the food web.
To illustrate the complex relationships within the temperate forest food web, consider the following example:
A white-tailed deer, a primary consumer, feeds on the leaves and twigs of a maple tree. The deer is preyed upon by a coyote, a secondary consumer. The coyote, in turn, is hunted by a mountain lion, a tertiary consumer. The mountain lion's feces and urine contribute to the nutrient cycle, providing essential nutrients for the maple tree to grow. Meanwhile, decomposers like fungi and bacteria break down the dead leaves and twigs, recycling nutrients that benefit the entire ecosystem.
This example highlights the interconnectedness of the food web, demonstrating how each species plays a vital role in maintaining the balance and health of the ecosystem.
| Trophic Level | Example Species |
|---|---|
| Producers | Oak trees, ferns, wildflowers |
| Primary Consumers | Deer, rabbits, squirrels, caterpillars |
| Secondary Consumers | Foxes, coyotes, owls, raccoons |
| Tertiary Consumers | Bears, mountain lions, hawks, eagles |
| Decomposers | Fungi, bacteria, earthworms |

In conclusion, the food web in the temperate forest is a complex and dynamic system, comprising multiple trophic levels and influenced by various abiotic factors. Understanding the relationships between species and their environment is essential for managing and conserving these ecosystems, ensuring the long-term health and biodiversity of the temperate forest.
What is the role of decomposers in the temperate forest food web?
+Decomposers, such as fungi, bacteria, and earthworms, play a crucial role in breaking down dead organic matter into nutrients that can be reused by producers. This process helps maintain soil fertility and supports the growth of plants, which in turn benefits the entire ecosystem.
How do abiotic factors influence the temperate forest food web?
+Abiotic factors like climate, soil quality, and topography can impact the growth and productivity of producers, which in turn affects the populations of consumers. For example, changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can alter the distribution and abundance of species, shaping the structure of the food web.
What is the importance of apex predators in the temperate forest food web?
+Apex predators, such as mountain lions and bears, play a vital role in regulating the populations of secondary consumers, which helps maintain the balance of the ecosystem. By controlling the numbers of secondary consumers, apex predators prevent any one species from dominating the ecosystem, ensuring the long-term health and biodiversity of the temperate forest.
By examining the complex relationships within the temperate forest food web, we can gain a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness of species and their environment, and work towards preserving the delicate balance of these ecosystems.


